Complying with the TCFD Recommendations
Recognizing that responding to climate change, which has a major impact on the environment, society and business activities, is an important issue, JAPAN POST BANK announced its agreement with the TCFD*1 Recommendations in April 2019. Since then, the Bank has incorporated various initiatives into its management strategies, increasing the level of its response to climate change.
- *1:
- Abbreviation of Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures. An organization established at the proposal of the Financial Stability Board for the purpose of thoroughly realizing corporate information disclosure pertaining to climate change, in which the representatives of the central banks and financial supervisory authorities, etc., of key nations participate.
Governance
- The status of climate change initiatives is discussed and reported by the Sustainability Committee (an advisory body to the Executive Committee) and the Executive Committee, and then reported to the Board of Directors.
- The Board of Directors makes decisions on important matters related to addressing climate change, including the establishment of the Basic Sustainability Policy, which stipulates that the Company will work to resolve environmental issues, including climate change, and to disclose information in a timely and appropriate manner, as well as resolutions on reducing GHG emissions and determining targets for the balance of ESG-themed investments and financing. In addition, the Board of Directors receives reports on the status of initiatives from the director in charge of sustainability, etc., and oversees the company's response to climate change from both quantitative and qualitative perspectives.
- The President and Representative Executive Officer, as "the person who represents Japan Post Bank and presides over its operations," is responsible for climate change-related matters and makes decisions on matters discussed at the Sustainability Committee, including revisions to the ESG Investment and Financing Policy and the annual plan for sustainability promotion, the company promotes sustainability management by making decisions on matters discussed at the Sustainability Committee, including revisions to the ESG Investment and Financing Policy and the annual plan for sustainability promotion.
- The following indicators related to climate change are incorporated into executive compensation. These indicators are applied to all executive officers, including the President and Representative Executive Officer.
- Balance of ESG-themed investments and financing: This indicators is related to ESG bonds and other bonds that use climate change mitigation and adaptation as a use of funds.
- ESG ratings from major ESG rating agencies (FTSE, MSCI, CDP, DJSI): These ESG ratings are based on questions related to climate change and other issues, and provide an objective assessment of the Bank's climate change initiatives.
Related Information
JAPAN POST BANK Environmental Policy
Strategy
JAPAN POST BANK has identified the risks and opportunities related to climate change as follows.
| Risks and Opportunities | Details | Period*2 | Financial impact*3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Risks |
|
Short term | Small |
| Transition Risks |
|
Medium to long term | Medium |
| Opportunities |
|
Short to long term | Medium |
- *2:
- The period of time until the applicable risk occurs or becomes more apparent. Short term: Less than one year; Medium term: 1–3 years; Long term: 3 or more years.
- *3:
- The financial impact on the balance sheet and profit and loss statement. Small: less than ¥1 billion per year; Medium: ¥1 billion to ¥10 billion per year; Large: ¥10 billion or more per year.
Related Information
- In order to identify the impact of climate change-related risks on the Bank’s finance portfolio, JAPAN POST BANK undertook a transition risk scenario analysis for the securities (bonds and equities) that comprise the majority of the portfolio. The impact of increased carbon costs on the earnings of investee companies for the subject period was calculated for each individual company, and the results of calculating the sum total of the impact is presented as follows.
- Looking ahead, JAPAN POST BANK will continue to monitor the impact of climate change and support the initiatives of investees through engagement and other means, while undertaking a variety of measures including analyses that take into consideration the long-term impact of climate change on an ongoing basis based on the aforementioned analysis.
The table below shows the balance and percentage of carbon-related assets and sustainable finance as a percentage of loans as of March 31, 2024.
(unit:billion)
| Carbon-related assets | Sustainable Finance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon-related assets outstanding | ¥358.8 | Sustainable Finance Outstanding | ¥172.3 | |
| Green Loans, Social Loans, Sustainable Loans |
¥68.0 | |||
| Sustainability-linked corporate loans | ¥19.4 | |||
| Others※ | ¥84.9 | |||
| Percentage of carbon-related assets | 5.2% | Percentage of Sustainable Finance | 2.5% | |
- *
- Positive impact finance, transition finance, credit for renewable energy sector, etc.
- note:
- Loan balance as of March 31, 2024 is ¥6,848.3 billion.
Transition Risks
| Scenario |
|
|---|---|
| Scope |
|
| Analytical Method |
|
| Internal Carbon Pricing |
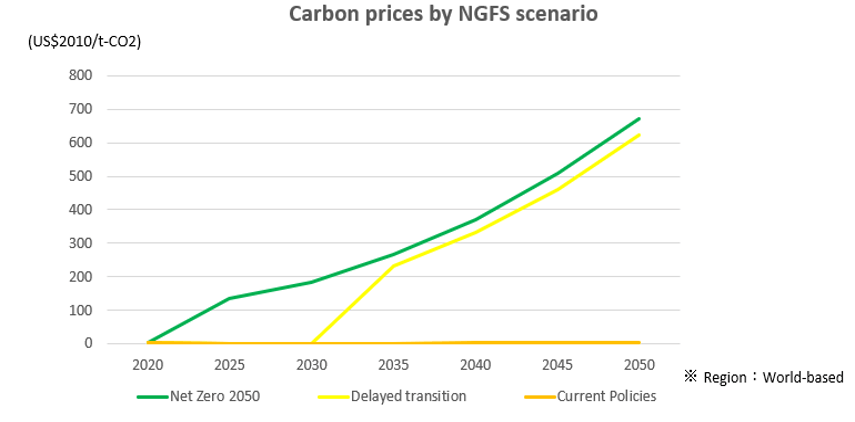
Under the "Net Zero 2050" scenario, the internal carbon pricing is set at approximately $135 (15,058 yen)/t-CO2 in FY2025. * Three future carbon price scenarios published by NGFS were used to calculate carbon costs (see figure below). |
| Target Period | Bonds: Up to the end of the redemption date of each bond Equities: Up to 2100 |
| Analysis Results | Approximately –¥600.0 billion (maximum amount of decrease in fair market value) |
| Financial Impact |
|
For physical risk, JAPAN POST BANK conducted a quantitative analysis of the impact on the Bank’s ATMs, devices at counters, and other equipment installed and owned by the Bank nationwide. According to inundation depth predictions and the current assumption of such water-related disasters as floods, the amount of damage to the Bank’s facilities was estimated at approximately ¥25 billion on a cumulative basis over the next 100 years. While climate change is expected to roughly double the frequency of floods under the 2°C scenario and increase the incidence of floods roughly four times under the 4°C scenario, the risk of damage to the Bank’s facilities on a simultaneous basis is considered low due to the spread of facilities over a nationwide network. Taking into account the aforementioned, the impact on JAPAN POST BANK’s financial strategies is expected to be limited.
Physical Risks
| Scenario | IPCC RCP2.6 (2°C scenario)*7 | IPCC RCP8.5 (4°C scenario)*7 |
|---|---|---|
| Scope |
|
|
| Analytical Method |
|
|
| Target Period | Over the next 100 years | |
| Analysis Results | Approximately –¥50 billion | Approximately –¥100 billion |
| Financial Impact |
|
|
- *4:
- Climate scenarios released in June 2021 by the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS).
- *5:
- Excluded from the scope of calculation in the event required data (GHG emissions, financial related data, etc.) is incomplete.
- *6:
- Costs incurred by investees as a result of an increase in the carbon price under the scenario.
- *7:
- Scenario of the average increase in global temperatures over the next 100 years announced by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
Risk Management
JAPAN POST BANK has introduced a Risk Appetite Framework (RAF) and positions risks related to climate change, etc., as one of the top risks facing the Bank. These risks are reflected in the Bank’s management plans, and the ESG team which has been established in the Corporate Planning Department acts as necessary following regular checks of the status of control.
JAPAN POST BANK is advancing global asset allocations based on its ESG Investment and Financing Policy, which is based on sectors with a significant impact on climate change and various international agreements, etc. In the years to come, the Bank will consider enhancing this policy from the perspective of fulfilling and contributing to climate change obligations as an institutional investor.
JAPAN POST BANK took steps to engage with companies that have a significant impact on climate change. Details of examples are presented as follows.
| Company | Main content of dialogue |
|---|---|
| Electricity sector Company A | Efforts are being made to achieve established GHG emission reduction targets. As a part of these efforts, steps are being taken to develop mixed combustion and other technologies with the aim of restarting nuclear power plants while garnering the understanding of local residents. |
Related Information
ESG Investment and Financing Policy
Metrics and Targets
To assess and manage risks related to climate change, we have set GHG emissions reduction targets. We have also set a target for the balance of ESG-themed investments and financing in order to assess and manage opportunities related to climate change. For more information, please visit under related information.
Related Information
Climate Change Initiatives: "Climate Change Metrics and Targets"